KEY STAGE 4 SC3 MATERIALS AND THEIR PROPERTIES Changing materials
2a) how the mixture of substances in crude oil, most of which are hydrocarbons, can be separated by fractional distillation
b) the use of some of the products from crude oil distillation as fuels -
Crude Oil is a MIXTURE of different compounds, in this case HYDROCARBONS (Compounds that contain Hydrogen and Carbon only) – Ensure you can explain the difference between Mixtures and Compounds. Mixtures can be separated by PHYSICAL methods such as filtration, distillation. The Hydrocarbons in Crude Oil are the important fuels and oil based products that our way of life depends on. For a virtual tour of an Oil refinery and its role see: http://www.schoolscience.co.uk/content/4/chemistry/petroleum/fawley/index.html
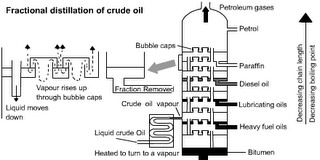
Crude Oil is separated by Fractional Distillation. Different Hydrocarbons have different BOILING POINTS. This means the different FRACTIONS can be separated by either heating the liquid to different temperatures and collecting the different products as they boil off or by collecting liquids as the CONDENSE at different temperatures.
The different fractions are put to different uses. Note that the fractions with the lower boiling points are thinner, lighter in colour and more flammable. They tend to be smaller molecules: For details see: http://www.schoolscience.co.uk/content/4/chemistry/petroleum/knowl/4/2index.htm?fractions.html
Hydrocarbons are split into ALKANES and ALKENES. Alkanes are said to be SATURATED because all the carbon atoms in the “spine” of the molecule are joined by single COVALENT bonds. Alkenes (Hint to remember: note the extra lines in an E versus an A) are have double bonds.
Alkane R–CH2–CH2–R CnH2n+2
Alkene R–CH=CH–R CnH2n
Source: http://www.cem.msu.edu/~reusch/VirtualText/nomen1.htm
Industrial scale fractional distillation
This uses condensation at different temperatures.
Source: http://lgfl.skoool.co.uk/examcentre.aspx?id=182
Larger molecules can be CRACKED into smaller more useful ones by the use of heating and catalysts.
Fractional Distillation should be a classroom experiment:
It can be simply done by heating a test tube and collection the distillate in a cooled receiver, taking note of the boiling temperature of each fraction or by the use of more complicated and professional apparatus.


Full details of a safer alternative to using Crude Oil see the CLEAPSS hazcard
An excellent presentation for classroom use is at:
http://lgfl.skoool.co.uk/content/keystage4/chemistry/pc/lessons/uk_ks4_oil_products/h-index.htm
No comments:
Post a Comment